what is the prognosis for malignant pleural effusion
An exudate or transudate. Diagnosis of malignant pleural mesothelioma typically occurs at an advanced stage and prognosis is poor.

Malignant Pleural Effusions Thoracic Key
Mesothelioma is characterized by malignant tumors that develop in the mesothelium a layer of protective tissue that covers several organs.

. The minimum volume of pleural fluid required to diagnose malignant pleural effusion. Malignant pleural effusion MPE is indicative of terminal malignancy with a uniformly fatal prognosis. Escape of a fluid into a part.
Malignant mesothelioma is an aggressive and incurable tumour caused by asbestos arising from mesothelial cells of the pleura peritoneum the lining of the abdominal cavity and rarely elsewhere. Pleural mesothelioma is the most common type of mesothelioma representing about 75 percent of cases. Pleural empyema is a collection of pus in the pleural cavity caused by microorganisms usually bacteria.
Lung cancer is the most common cause of malignant pleural effusion followed by breast cancer. The gold standard for diagnosis of MPE is positive PF cytology or pleural biopsy. The presence of a malignant pleural effusion carries the worst long-term prognosis when one considers other causes of a bloody pleural effusion.
Often two distinct compartments of tumour microenvironment the effusion and disseminated. Alongside the treatment of the underlying disease the specific treatment of pleural effusion ranges from. Malignant pleural effusion an excess buildup of fluid containing cancer cells in the pleural cavity.
It is one of the various kinds of pleural effusionThere are three stages. It is the most common manifestation of pleural disease with etiologies ranging from cardiopulmonary disorders to symptomatic inflammatory or malignant diseases requiring urgent evaluation and trea. Level V Review.
Tumor markers in undiagnosed pleural effusions. There is no single demographic affected as there are many underlying causes of pericardial effusion. 1100 and 1400 mL of pleural effusion.
Serum tumour markers are used in clinical practice for screening diagnosis prognosis and management in a number of malignancies 42 but PF tumour markers are not routinely used in clinical practice. The outcome of a hemothorax is determined by both the extent of the bleeding and the underlying cause. It accounts for 125000 hospital admissions per year in the United States 12The presence of MPE always.
Often it happens in the context of a pneumonia injury or chest surgery. Fibrinopurulent when fibrous septa form. Cytology performed on pleural fluid can confirm the presence of a malignant pleural effusion.
Peritoneal mesothelioma is the second most common type consisting of. Benign effusions can be cured but if the cause is a malignancy the prognosis is very poor. Genetic studies can be performed in cases of genetic diseases that predispose patients to a hemothorax.
The four types of mesothelioma are identified by the location where tumors develop. Pericardial effusion the accumulation of an abnormally large amount of pericardial fluid in the pericardium. Accumulated fluid from a pericardial effusion evacuated by the.
The prognosis depends on the cause of the pleural effusion. They are usually found in the context of gas or blood in the pleural cavity and do not exclude a malignant cause. We were aware from our own clinical practice that the prognosis of patients presenting with malignant pleural effusions was very variable.
Most lymphocytic pleural effusions are due to 14. Malignant pleural effusion MPE is a common and disabling complication of cancer. Chyliform effusion see chylothorax.
Systemic cytotoxic therapy with platinum and pemetrexed has been the backbone of therapy for more than a decade. Chylous effusion see chylothorax. Chylothorax a buildup of chyle.
Clinical presentation of pericardial effusions does not relate so much to the size of the effusion but rather the speed at which the fluid has accumulated as slow gradual accumulation allows the pericardium to. Liang QL Shi HZ Qin XJ et al. Precise differential diagnostic categorization is essential as the treatment and prognosis of pleural effusion largely depend on its cause.
Irrespective of the cause of the malignant pleural effusion. The treatment of pleural effusions is usually targeted to the underlying. Pleural mesothelioma lungs peritoneal mesothelioma abdomen pericardial mesothelioma heart and mesothelioma of the tunica vaginalis testes.
A number of studies had looked at individual prognostic factors but a validated prognostic tool was not available. Pleural effusion an excess buildup of fluid in the pleural cavity. Diagnostic accuracy of tumour markers for malignant pleural effusion.
Pleural malignant mesothelioma patients may be diagnosed with a co-occurring asbestos-related condition which can impact symptom onset. A pleural effusion is an abnormal collection of fluid in the pleural space resulting from excess fluid production or decreased absorption or both. Pleural effusion occurs when an abnormal amount of fluid collects in between the two layers of the pleura.
When pleural effusions are inadequately treated this can result in an empyema sepsis and even a trapped lung. This fluid can compress the lungs making it difficult to breathe. Exudative when there is an increase in pleural fluid with or without the presence of pus.
Pleural effusion dyspnoea pericardial effusion and sepsis each occurred in three 4 patients and constrictive. Some patients survive only a few weeks whereas others live for years after diagnosis.

Malignant Pleural Effusion 03102017 Youtube
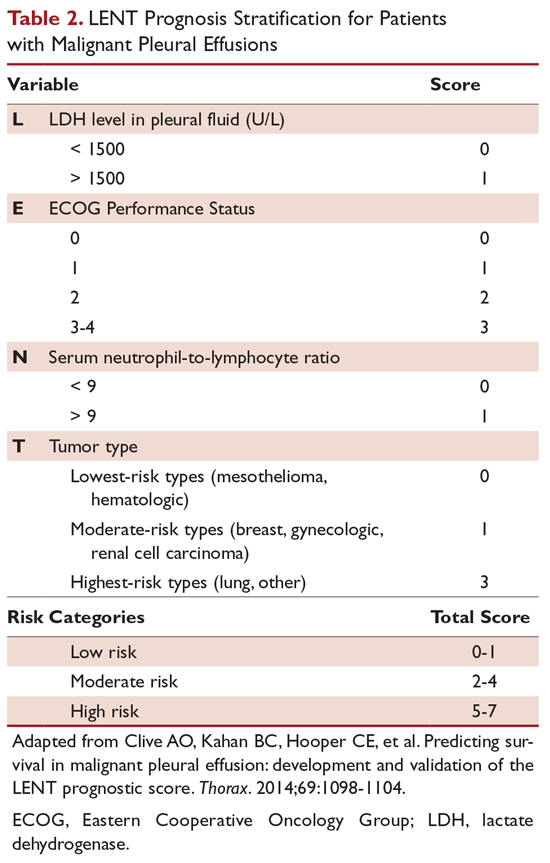
Malignant Pleural Effusion Evaluation And Diagnosis Pulmonary Health Hub

Prognostic Impact Of Malignant Pleural Effusion At Presentation In Patients With Metastatic Non Small Cell Lung Cancer Journal Of Thoracic Oncology

Management Of Malignant Pleural Effusions The Figure Is Modified From Download Scientific Diagram
The Current Aetiology Of Malignant Pleural Effusion In The Western Cape Province South Africa
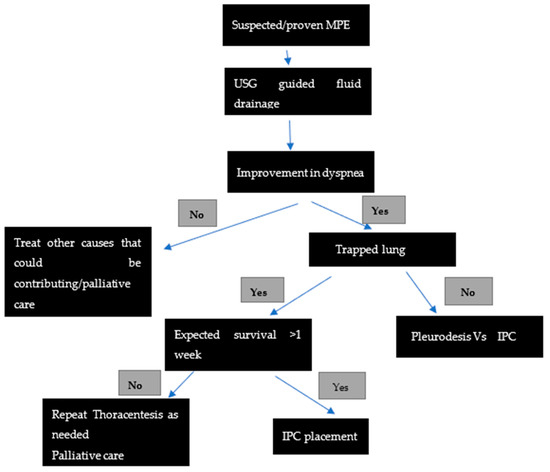
Jcm Free Full Text Malignant Pleural Effusions Mdash A Review Of Current Guidelines And Practices

Ers Eacts Statement On The Management Of Malignant Pleural Effusions European Respiratory Society

Malignant Pleural Effusion Management Keeping The Flood Gates Shut The Lancet Respiratory Medicine

Overall Survival Probability According To Malignant Pleural Effusion Download Scientific Diagram

Treatment Options For Malignant Pleural Effusions Download Table

Mortality Among Patients With Pleural Effusion Undergoing Thoracentesis European Respiratory Society
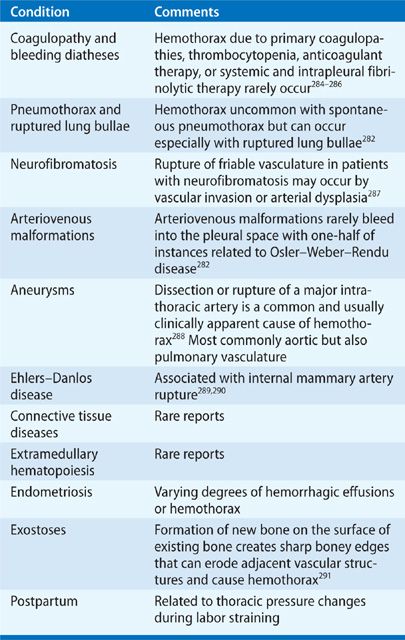
Malignant Pleural Effusions Thoracic Key

The Diagnostic Steps In Suspected Malignant Pleural Effusion Table 1 Download Scientific Diagram
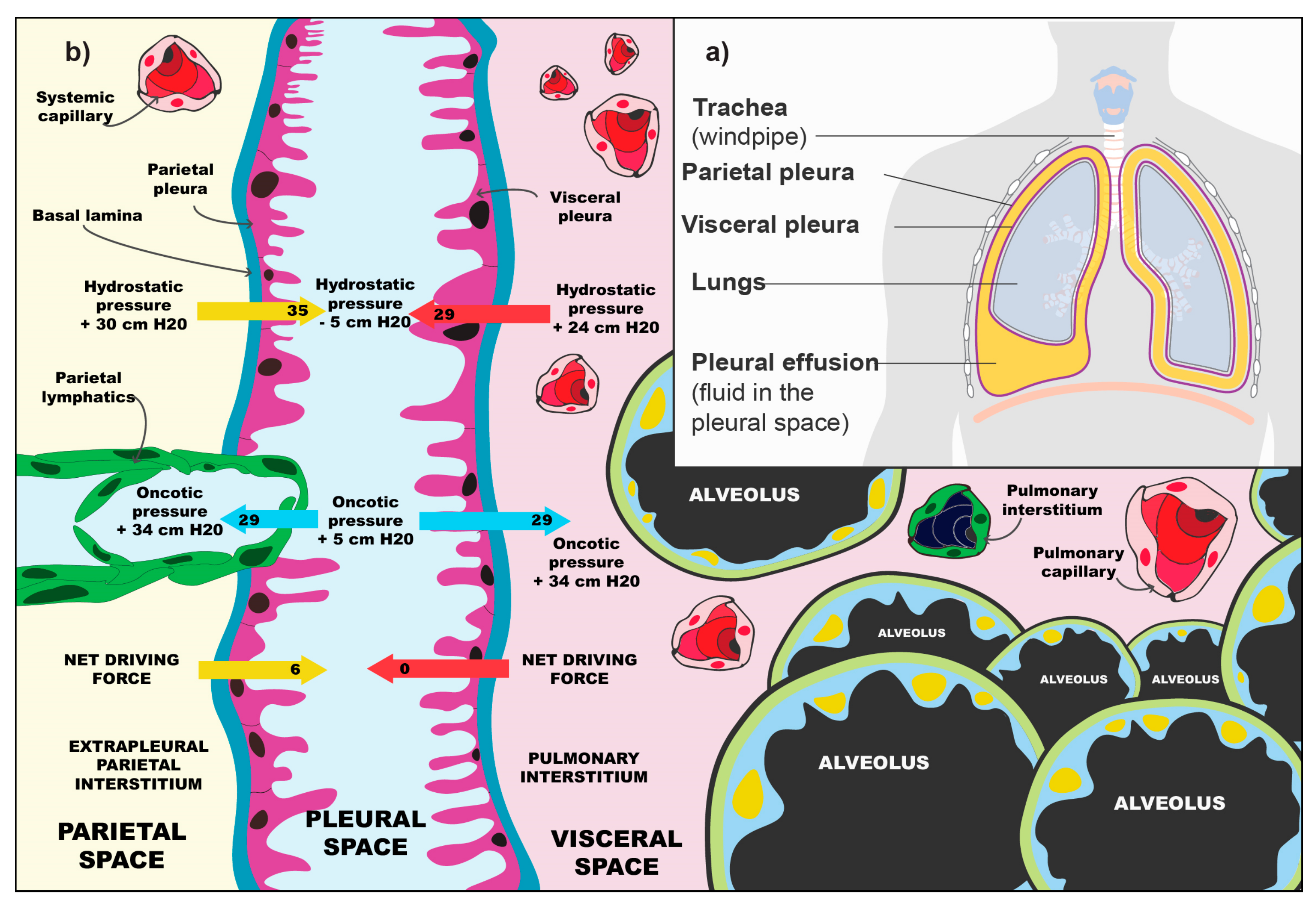
Medicina Free Full Text Malignant Pleural Effusion And Its Current Management A Review Html
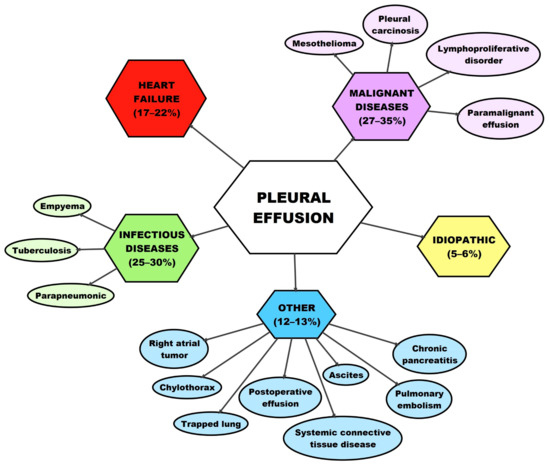
Medicina Free Full Text Malignant Pleural Effusion And Its Current Management A Review Html
Malignant Pleural Effusion Still A Long Way To Go Researcher An
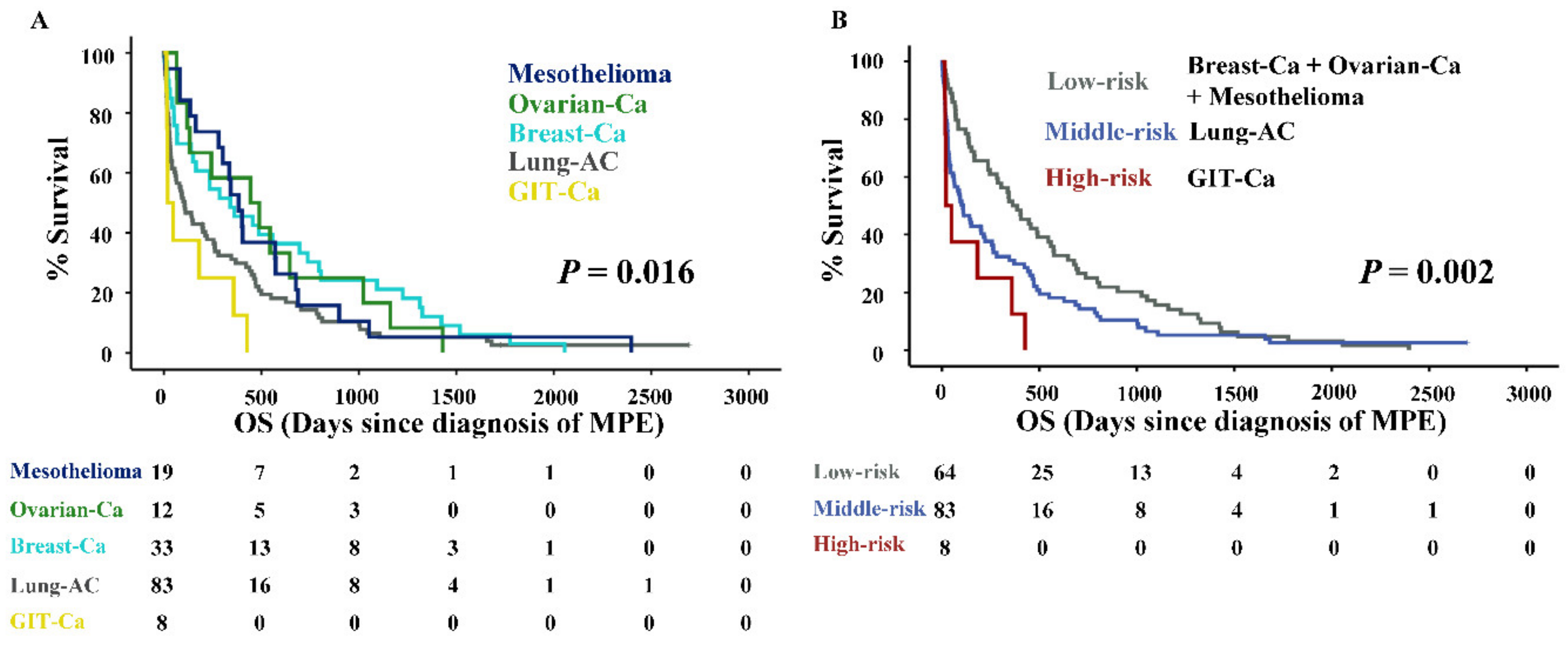
Cancers Free Full Text Prognostic Immune Cell Profiling Of Malignant Pleural Effusion Patients By Computerized Immunohistochemical And Transcriptional Analysis Html

Pdf Malignant Pleural Effusion Medical Approaches For Diagnosis And Management Semantic Scholar

Prognostic Value And Therapeutic Implications Of Pleural Carcinosis And Malignant Pleural Effusion In Advanced Epithelial Ovarian Cancer Anticancer Research